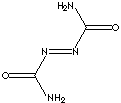
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
UN NO.
3242
TOXICITY
Oral ra LD50: 6400 mg/kg
SMILES
CLASSIFICATION
Blowing agent
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
MELTING POINT
SOLUBILITY IN WATER
REFRACTIVE INDEX
225 C
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION
GENERAL
DESCRIPTION:
Azo is the
prefix for the group -N=N- or a combining form of azote which share the
core azobenzene structure. Azo compounds have a general
molecular formula of R-N=N-R', where R is aryl,
heteroaryl, -CH=C(OH)- or aliphatic. The extended delocalization of
electrons in the benzene and azo groups forms a conjugated system absorbing
visible frequencies of light. Aromatic groups provide characteristic colors of
red, orange, and yellow. This is the fundamental structure
of azo dyes. Aliphatic azo compounds are unstable and
the loss of nitrogen gas occurs by the simultaneous
cleavage of carbon-nitrogen bonds, resulting in carbon-centered
radicals. some aliphatic azo compounds are utilized as radical initiators. Azobisisobutyronitrile
is a typical initiator of free radical reactions for
the production of polymer (polyvinyl chloride, polyacrylonitrile,
polyvinyl alcohol and synthetic fibers) and as a blowing
agent for plastics and elastomers.
Azodicarbonamide, releasing nitrogen gas, is a general foaming agent for rubbers and plastics such as PVC, EVA, polyolefin, polystyrene products. (Its temperature of decomposition is 205 - 215 C). Food grade of Azodicarbonamide is used as a flour aging and bleaching ingredient in cereal flours and dough conditioner in baking bread. It reacts with moist flour as an oxidizing agent. Azodicarbonamide acts as a hydrogen acceptor, converting to biurea. The United States allows azodicarbonamide to be added to flour at levels up to 45 ppm. Use of azodicarbonamide as a food additive is banned in Australia and in Europe. The pharma grade of Azodicarbonamide molecule is used as an Anti-HIV agent, Anti-Infective Agent, Anti-Retroviral Agent, Antiviral Agent, Immunologic Factor, Immunosuppressive Agent .
SALES SPECIFICATION
APPEARANCE
ASSAY
97.0% min
ASH
0.2% max
200 C min
210 min (ml/g)
HEAT LOSS
0.3% max
12 - 14 um or 7 - 9um or 6 - 8um
WATER
0.25% max
Blowing agents, also called foaming agents, can be classified as Physical and Chemical Blowing Agents. Physical blowing agents are not under chemical changes during processing. Physical blowing agents are in forms of liquid or compressed gas which will transfer state into gases or low boiling liquid during processing causing resins into cellular structure. Chemical Blowing Agents are mainly solid form of hydrazine derivatives include Azodicarbonamide; p,p'-Oxybis(benzenesulfonyl hydrazide); 5-Phenyltetrazole; p-Toluene sulfonyl semicarbazide; Trihydrazine Triazine; They commonly release gases such as nitrogen, carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide or ammonia. But ammonia is not desirable as it effects on degrade of resins. There are nonazo blowing agents releasing carbon dioxide such as sodium borohydride.
Blowing Agent Class
- Azo Compounds
- Azodicarbonamide (CAS RN: 123-77-3)
- Hydrazine Compounds
- p-Toluenesulfonylhydrazide (CAS RN: 1576-35-8)
- p,p'-Oxybis (Benzenesulfonylhydrazide) (CAS RN: 80-51-3)
- Benzenesulfonyl Hydrazide (CAS RN: 80-17-1)
- p-Toluenesulfonyl acetone hydrazone
- Carbazides
- p-Toluenesulfonylsemicarbazide (CAS RN: 10396-10-18)
- p,p'-Oxybis (Benzenesulfonylsemicarbazide)
- Tetrazoles
- 5-Phenyltetrazole (CAS RN: 18039-42-4)
- Nitroso Compounds
- N,N��-Dinitroso-pentamethylenetetramine (CAS RN: 101-25-7)
- Carbonates
- Sodium Bicarbonate (CAS RN: 144-55-8)
PRICE INFORMATION